스프링 배치(스프링 Boot 기반)삽질기 2탄 - Spring Batch Meta-data Schema 커스터마이징
회사에서 스프링 배치를 이용한 배치성 프로그램을 제작을 하게 되었습니다. 스프링배치를 많이 다뤄본 경험이 부족하여 이번 프로젝트를 진행하며 많은 삽질을 경험했는데, 삽질 내용을 남기고자 포스팅을 시작합니다. 총 3편으로 포스팅을 진행하려 합니다. 오늘 포스팅은 2번째 포스팅으로써 Spring Batch Meta-data Schema를 커스터마이징 하는 방법에 대해서 포스팅 하고자 합니다.
시작하며
스프링배치는 아래와 같은 테이블구조로 메타데이터를 자동으로 관리해 줍니다. 따라서 배치를 시작할때 자동으로 org.springframework.batch.core 패키지에 있는 schema-*.sql 파일을 참조해서 스키마를 디자인 해주게 됩니다.
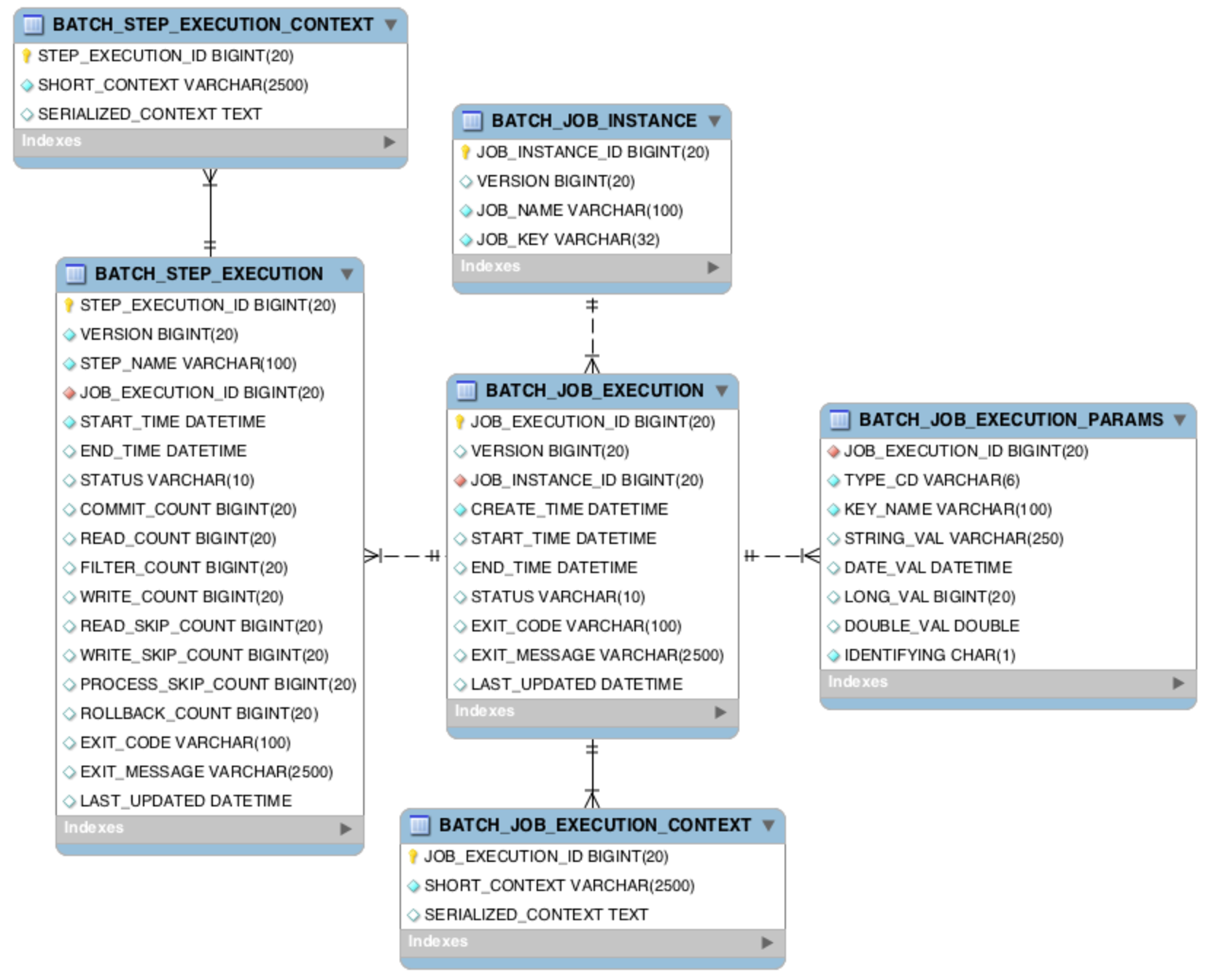
출처 : http://docs.spring.io/spring-batch/reference/html/metaDataSchema.html
오늘 포스팅에서는 스프링 배치 Meta-data Schema를 커스터마이징 하는 방법에 대해서 알아보고자 합니다.
org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-batch Dependency 까보기!
먼저 배치 스키마를 커스터마이징을 해주기 위해서는 org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-batch 패키지가 어떤식으로 설정을 주는지를 알아야 합니다.
해당 패키지의 의존성이 어떻게 걸려있는지 먼저 확인하고자 pom.xml을 찾아보겠습니다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starters</artifactId>
<version>1.5.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-batch</artifactId>
<name>Spring Boot Batch Starter</name>
<description>Starter for using Spring Batch</description>
<url>http://projects.spring.io/spring-boot/</url>
<organization>
<name>Pivotal Software, Inc.</name>
<url>http://www.spring.io</url>
</organization>
<properties>
<main.basedir>${basedir}/../..</main.basedir>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.batch</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-batch-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.basepom.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>duplicate-finder-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>duplicate-dependencies</id>
<phase>validate</phase>
<goals>
<goal>check</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<exceptions>
<exception>
<conflictingDependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>xpp3</groupId>
<artifactId>xpp3_min</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>xmlpull</groupId>
<artifactId>xmlpull</artifactId>
</dependency>
</conflictingDependencies>
</exception>
</exceptions>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
출처 : https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/blob/master/spring-boot-starters/spring-boot-starter-batch/pom.xml
해당 패키지에 주입된 의존성을 확인해보니
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.batch</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-batch-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
spring-boot-start, spring-boot-starter-jdbc, spring-batch-core 세가지의 의존성을 가지고 있습니다.
17:25:35.466 [WARN ] [main] [o.s.b.a.batch.BasicBatchConfigurer] [createJobRepository:150] - JPA does not support custom isolation levels, so locks may not be taken when launching Jobs
17:25:35.473 [INFO ] [main] [o.s.b.c.r.s.JobRepositoryFactoryBean] [afterPropertiesSet:183] - No database type set, using meta data indicating: H2
17:25:35.669 [INFO ] [main] [o.s.b.c.l.support.SimpleJobLauncher] [afterPropertiesSet:195] - No TaskExecutor has been set, defaulting to synchronous executor.
17:25:35.714 [INFO ] [main] [o.s.jdbc.datasource.init.ScriptUtils] [executeSqlScript:442] - Executing SQL script from class path resource [org/springframework/batch/core/schema-h2.sql]
17:25:35.730 [INFO ] [main] [o.s.jdbc.datasource.init.ScriptUtils] [executeSqlScript:508] - Executed SQL script from class path resource [org/springframework/batch/core/schema-h2.sql] in 16 ms.
그리고 로그를 확인해보니 BasicBatchConfigurer Bean에서 스키마에 대한 설정을 시작하는 것으로 보입니다. 해당 Bean을 찾아서 열어보겠습니다.
/*
* Copyright 2012-2017 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.BatchConfigurer;
import org.springframework.batch.core.explore.JobExplorer;
import org.springframework.batch.core.explore.support.JobExplorerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.batch.core.launch.JobLauncher;
import org.springframework.batch.core.launch.support.SimpleJobLauncher;
import org.springframework.batch.core.repository.JobRepository;
import org.springframework.batch.core.repository.support.JobRepositoryFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionManagerCustomizers;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
/**
* Basic {@link BatchConfigurer} implementation.
*
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Andy Wilkinson
* @author Kazuki Shimizu
*/
public class BasicBatchConfigurer implements BatchConfigurer {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(BasicBatchConfigurer.class);
// 요녀석 같은 느낌!
private final BatchProperties properties;
private final DataSource dataSource;
private final EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory;
private PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
private final TransactionManagerCustomizers transactionManagerCustomizers;
private JobRepository jobRepository;
private JobLauncher jobLauncher;
private JobExplorer jobExplorer;
/**
* Create a new {@link BasicBatchConfigurer} instance.
* @param properties the batch properties
* @param dataSource the underlying data source
* @param transactionManagerCustomizers transaction manager customizers (or
* {@code null})
*/
protected BasicBatchConfigurer(BatchProperties properties, DataSource dataSource,
TransactionManagerCustomizers transactionManagerCustomizers) {
this(properties, dataSource, null, transactionManagerCustomizers);
}
/**
* Create a new {@link BasicBatchConfigurer} instance.
* @param properties the batch properties
* @param dataSource the underlying data source
* @param entityManagerFactory the entity manager factory (or {@code null})
* @param transactionManagerCustomizers transaction manager customizers (or
* {@code null})
*/
protected BasicBatchConfigurer(BatchProperties properties, DataSource dataSource,
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory,
TransactionManagerCustomizers transactionManagerCustomizers) {
this.properties = properties;
this.entityManagerFactory = entityManagerFactory;
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.transactionManagerCustomizers = transactionManagerCustomizers;
}
@Override
public JobRepository getJobRepository() {
return this.jobRepository;
}
@Override
public PlatformTransactionManager getTransactionManager() {
return this.transactionManager;
}
@Override
public JobLauncher getJobLauncher() {
return this.jobLauncher;
}
@Override
public JobExplorer getJobExplorer() throws Exception {
return this.jobExplorer;
}
@PostConstruct
public void initialize() {
try {
this.transactionManager = createTransactionManager();
this.jobRepository = createJobRepository();
this.jobLauncher = createJobLauncher();
this.jobExplorer = createJobExplorer();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to initialize Spring Batch", ex);
}
}
protected JobExplorer createJobExplorer() throws Exception {
JobExplorerFactoryBean jobExplorerFactoryBean = new JobExplorerFactoryBean();
jobExplorerFactoryBean.setDataSource(this.dataSource);
String tablePrefix = this.properties.getTablePrefix();
if (StringUtils.hasText(tablePrefix)) {
jobExplorerFactoryBean.setTablePrefix(tablePrefix);
}
jobExplorerFactoryBean.afterPropertiesSet();
return jobExplorerFactoryBean.getObject();
}
protected JobLauncher createJobLauncher() throws Exception {
SimpleJobLauncher jobLauncher = new SimpleJobLauncher();
jobLauncher.setJobRepository(getJobRepository());
jobLauncher.afterPropertiesSet();
return jobLauncher;
}
protected JobRepository createJobRepository() throws Exception {
JobRepositoryFactoryBean factory = new JobRepositoryFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(this.dataSource);
if (this.entityManagerFactory != null) {
logger.warn(
"JPA does not support custom isolation levels, so locks may not be taken when launching Jobs");
factory.setIsolationLevelForCreate("ISOLATION_DEFAULT");
}
String tablePrefix = this.properties.getTablePrefix();
if (StringUtils.hasText(tablePrefix)) {
factory.setTablePrefix(tablePrefix);
}
factory.setTransactionManager(getTransactionManager());
factory.afterPropertiesSet();
return factory.getObject();
}
protected PlatformTransactionManager createTransactionManager() {
PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager = createAppropriateTransactionManager();
if (this.transactionManagerCustomizers != null) {
this.transactionManagerCustomizers.customize(transactionManager);
}
return transactionManager;
}
private PlatformTransactionManager createAppropriateTransactionManager() {
if (this.entityManagerFactory != null) {
return new JpaTransactionManager(this.entityManagerFactory);
}
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(this.dataSource);
}
}
해당 Bean을 까보니 여러가지 Batch를 실행하기 위한 설정들을 해주고 있습니다. 그 중에서 batch관련 properties를 설정해주는 Bean은 BatchProperties 해당 Bean을 통해서 설정을 주는 듯 합니다.
/*
* Copyright 2012-2017 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
/**
* Configuration properties for Spring Batch.
*
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Eddú Meléndez
* @author Vedran Pavic
* @since 1.2.0
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.batch")
public class BatchProperties {
// 찾았다!
private static final String DEFAULT_SCHEMA_LOCATION = "classpath:org/springframework/"
+ "batch/core/schema-@@platform@@.sql";
/**
* Path to the SQL file to use to initialize the database schema.
*/
private String schema = DEFAULT_SCHEMA_LOCATION;
/**
* Table prefix for all the batch meta-data tables.
*/
private String tablePrefix;
private final Initializer initializer = new Initializer();
private final Job job = new Job();
public String getSchema() {
return this.schema;
}
public void setSchema(String schema) {
this.schema = schema;
}
public String getTablePrefix() {
return this.tablePrefix;
}
public void setTablePrefix(String tablePrefix) {
this.tablePrefix = tablePrefix;
}
public Initializer getInitializer() {
return this.initializer;
}
public Job getJob() {
return this.job;
}
public class Initializer {
/**
* Create the required batch tables on startup if necessary. Enabled automatically
* if no custom table prefix is set or if a custom schema is configured.
*/
private Boolean enabled;
public boolean isEnabled() {
if (this.enabled != null) {
return this.enabled;
}
boolean defaultTablePrefix = BatchProperties.this.getTablePrefix() == null;
boolean customSchema = !DEFAULT_SCHEMA_LOCATION
.equals(BatchProperties.this.getSchema());
return (defaultTablePrefix || customSchema);
}
public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) {
this.enabled = enabled;
}
}
public static class Job {
/**
* Comma-separated list of job names to execute on startup. By default, all Jobs
* found in the context are executed.
*/
private String names = "";
public String getNames() {
return this.names;
}
public void setNames(String names) {
this.names = names;
}
}
}
BatchProperties Bean을 까보니 DEFAULT_SCHEMA_LOCATION 라는 멤버변수가 기본 .sql 파일을 읽어와서 스프링 배치 스키마를 만들어 주고 있는것을 확인했습니다.
Bean Overriding을 통해서 기본 스키마 바꿔주기
지금까지 스프링 배치 관련 패키지들을 들여다 보면서 어떤식으로 스프링 배치 meta-data 스키마를 설정해주고 있는지 확인했습니다.
기본 .sql파일을 설정해주는 빈은 BatchProperties빈인 것을 확인했고 그렇다면 해당 빈을 오버라이딩 해서 BatchProperties 빈의 setSchema 메소드를 통해서 원하는 .sql파일을 설정해주면 될 것 같습니다.
@Configuration
@EnableBatchProcessing
public class BatchConfig {
@Autowired
private JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory;
@Autowired
private StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory;
@Bean
@Primary
public BatchProperties batchProperties () {
final String SCHEMA_LOCATION = "classpath:custom_batch_schema-h2.sql";
BatchProperties batchProperties = new BatchProperties();
batchProperties.setSchema(SCHEMA_LOCATION);
return batchProperties;
}
...
}
위와 같이 @Primary 어노테이션을 이용해서 BatchProperties 빈을 오버라이딩 해주어 제가 원하는 schema .sql 파일을 바라보도록 설정해주었습니다.
그럼 설정이 제대로 적용되었는지 실행해보겠습니다.
17:51:44.671 [INFO ] [main] [o.s.jdbc.datasource.init.ScriptUtils] [executeSqlScript:442] - Executing SQL script from class path resource [custom_batch_schema-h2.sql]
17:51:44.689 [INFO ] [main] [o.s.jdbc.datasource.init.ScriptUtils] [executeSqlScript:508] - Executed SQL script from class path resource [custom_batch_schema-h2.sql] in 18 ms.
로그에서 보이는 것과 같이 설정이 잘 반영된 것을 보실 수 있습니다.
마치며
이런식으로 배치 설정 빈들을 확인한 후 BatchProperties 빈을 오버라이딩 하여 원하는 배치 스키마를 작성하는 방법을 살펴봤습니다.
메타데이터를 db를 보게하거나 하는 설정들도 배치 설정 빈들이 어떻게 돌아가는지만 확인한다면 위에서 설명드린 방법과 유사한 방식으로 얼마든지 커스터마이징이 가능해집니다.
저와 같은경우는 필드의 크기를 더 크게 해주기 위해서 해당 방법을 이용해서 batch schema를 커스터마이징 하였습니다.
다음 포스팅에서는 마지막으로 step간 데이터 공유를 할때, ExecutionContext를 이용하지 않고 다른 방법으로 데이터를 공유하는 방식을 소개해드리고자 합니다.
